Spartina® (tirzepatide): The First and Only Dual GIP and GLP‑1 Receptor Agonist Approved for the Treatment of Adults with Type 2 Diabetes
Indicated for Adults with Type 2 Diabetes
Spartina is indicated for adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus, as an adjunct to diet and exercise.
- Not studied in patients with history of pancreatitis
Key Benefits Mechanistically
Review ADA2025 Diabetes Guideline
Mechanism Behind Once-Weekly Dosing
Spartina® (tirzepatide) is structurally engineered with a C20 fatty acid side chain, which facilitates high-affinity binding to serum albumin. This molecular modification significantly prolongs its elimination half-life, allowing for once-weekly subcutaneous administration and sustained therapeutic efficacy for throughout the week.
Pharmacokinetics
- After injection, peak plasma concentrations are reached within approximately 8–72 hours.
- With a half-life of ~5 days, Spartina reaches steady-state plasma levels after about 4 weeks of weekly dosing.
Mechanism of Action
Dual Pathway Activation for Enhanced Glycemic Control
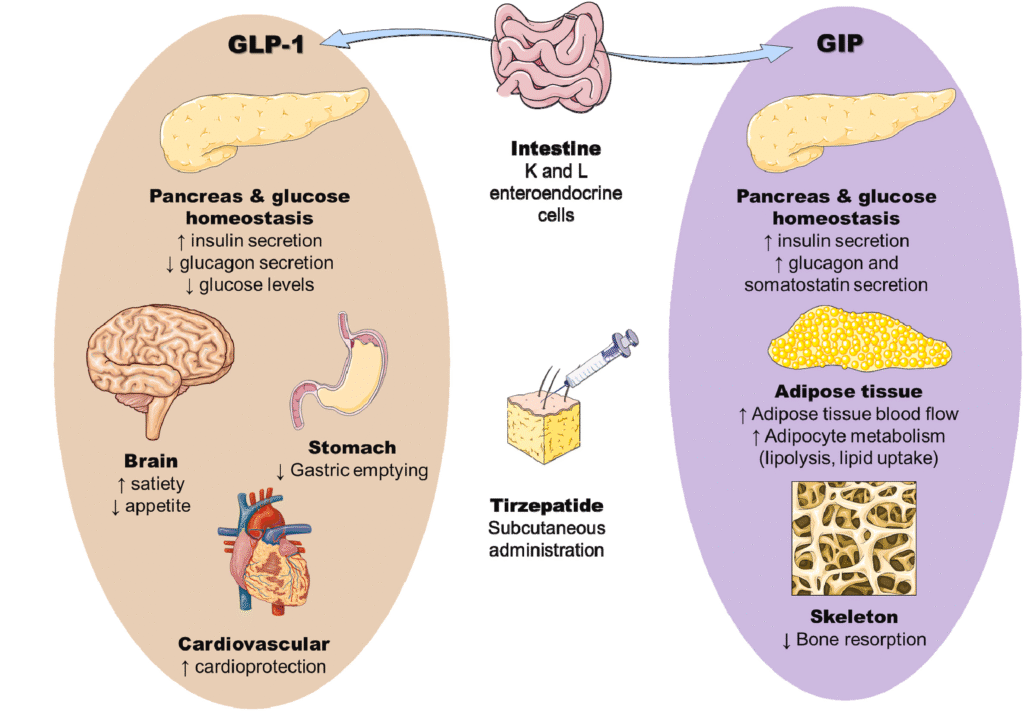
- GIP and GLP-1 are incretin hormones.
- By activating both GLP-1 and GIP receptors on pancreatic β-cells, tirzepatide enhances glucose-dependent insulin secretion, harnessing the incretin effect to improve glycemic control.
- In vitro, tirzepatide activates the GIP receptor with potency similar to native GIP, whereas its GLP‑1 receptor potency is approximately 5–13‑fold lower than native GLP‑1.
Systemic Actions:
- Stimulates insulin secretion
- Improves insulin sensitivity
- Reduces food intake
- lowers fasting and postprandial glucagon levels
- Delays gastric emptying (This effect is most pronounced at the beginning of the treatment.)
Clinical Effectiveness
Understanding the timeline, response, and dose relationships of tirzepatide therapy in type 2 diabetes.
A1C
Sustained A1C and weight reduction in patients with type 2 diabetes throughout clinical trials
Up to -2.58%
Reduction in A1C level by Tirzepatide 15 mg
Percentage of patients with A1C <7%
86%
Up to -2.4%
Reduction in A1C level by Tirzepatide 10 mg
Percentage of patients with A1C <7%
86%
Up to -2.4%
Reduction in A1C level by Tirzepatide 5 mg
Percentage of patients with A1C <7%
82%
Clinical trial data reveals that tirzepatide’s effects manifest early and are sustained over time:
- In the SURPASS-3 study, participants on tirzepatide reached HbA1c <7.0% in a median time of just 8.1 weeks, regardless of dose (5, 10, or 15 mg)
- Weight reduction occurred in a dose- and time-responsive manner, with the most rapid changes observed at higher doses:
- At 5 mg, ≥5% weight loss was achieved by week 16
- At 10 mg and 15 mg, the same threshold was reached as early as week 12.4
Due to its rapid achievement of glycemic and weight reduction targets, tirzepatide is an attractive option for clinicians seeking early metabolic control in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Clinical trials of tirzepatide show dose‑dependent improvements in HbA1c and weight; higher doses result in greater reductions.
- After initiating tirzepatide at 2.5 mg once weekly, the dose can be increased by 2.5‑mg increments every 4 weeks; each increase produces additional reductions in HbA1c and body weight, a benefit for patients with:
- Inadequate control on oral agents
- Plateauing response to prior GLP-1 RAs
- Progressive metabolic deterioration
Clinicians can titrate dose upward every 4 weeks, allowing customized treatment intensification aligned with patient tolerability and need
Clinical trials and their open-label extensions demonstrate that tirzepatide provides sustained reductions in HbA1c and body weight for up to two years, supporting its long-term efficacy in type 2 diabetes management.:
- Clinical benefits observed in these studies:
- Long-term glycemic control
- Sustained weight loss
- Consistent safety profile
This aligns with long-term management goals in type 2 diabetes and supports Spartina as a maintenance therapy after reaching target HbA1c and weight thresholds.
Safety Information
Boxed Warning
- Thyroid C-cell tumors observed in rats (dose- and time-dependent).
- Unknown relevance to humans.
- Contraindicated in:
- Personal/family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC)
- Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Syndrome Type 2 (MEN 2)
Monitoring
Routine serum calcitonin or ultrasound for MTC is uncertain in value and may lead to unnecessary interventions
Other Warnings
- Acute Pancreatitis:
Cases have been reported with tirzepatide; caution is advised in patients with a history of pancreatitis. Discontinue if pancreatitis is suspected or confirmed. - Hypoglycaemia:
Increased risk when used with insulin or sulfonylureas; dose adjustment of these agents may be necessary to reduce the risk. - Gastrointestinal Effects:
Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, which may lead to dehydration and renal complications. Adequate hydration is recommended, especially in elderly patients. - Severe Gastrointestinal Disease:
Tirzepatide has not been studied in patients with severe GI disorders (e.g. gastroparesis) and should be used with caution. - Diabetic Retinopathy:
Use with caution in patients with active or untreated proliferative diabetic retinopathy or macular edema; close monitoring is advised. - Aspiration Risk with Anaesthesia:
Delayed gastric emptying may increase aspiration risk during general anaesthesia or deep sedation; consider this before procedures.
Dosing and Administration
Start with 2.5 mg once weekly for 4 weeks
Increase to 5 mg weekly
Can further increase in 2.5 mg increments every 4 weeks if needed
Maximum dose: 15 mg weekly
If missed dose remembered within 4 days, take it as soon as possible
If >4 days, skip and continue with regular schedule
Maintain minimum 3-day gap between doses
Abdomen: At least 5 cm away from the navel.
Thigh: The front of the thigh, 5 cm distal to the groin and 5 cm proximal to the knee
Upper Arm: Inject into the middle area of the outer and back side of the upper arm; this site is typically used when the injection is given by someone else.
Rotate injection sites with each dose.
Switching from Other GLP-1 RAs
Start Spartina at 2.5 mg weekly
Can initiate Spartina at 2.5 mg or 5 mg, depending on clinical judgment and tolerability
Ideal Patient Profile
Who Should Use Spartina?
- Adults with type 2 diabetes
- Patients with elevated glucose despite lifestyle and oral agents
- Patients who may benefit from weight loss
- Those who require weekly instead of daily therapy
Not suitable for patients with:
MEN2, MTC, pancreatitis history, severe GI diseases, or pediatric patients
References
– Tirzepatide – Prescribing information
– Ludvik B, Giorgino F, E, et al. Once-weekly tirzepatide versus once-daily insulin degludec as add-on to metformin with or without SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes(SURPASS-3): a randomised, open-label, parallel-group, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;398(10300):583-598. doi:10.1016/50140-6736(21)01443-4
– Del Prato S, Kahn SE, Pavo I, Weerakkody GJ, Yang Z, Doupis J, Aizenberg D, Wynne AG, Riesmeyer JS, Heine RJ, Wiese RJ; SURPASS-4 Investigators. Tirzepatide versus insulin glargine in type 2 diabetes and increased cardiovascular risk (SURPASS-4): a randomised, open-label, parallel-group, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021 Nov 13;398(10313):1811-1824. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02188-7. Epub 2021 Oct 18. PMID: 34672967.
